Impressive Tips About How To Stop Yum Update

Use a text editor such as vi to edit /etc/yum.conf:
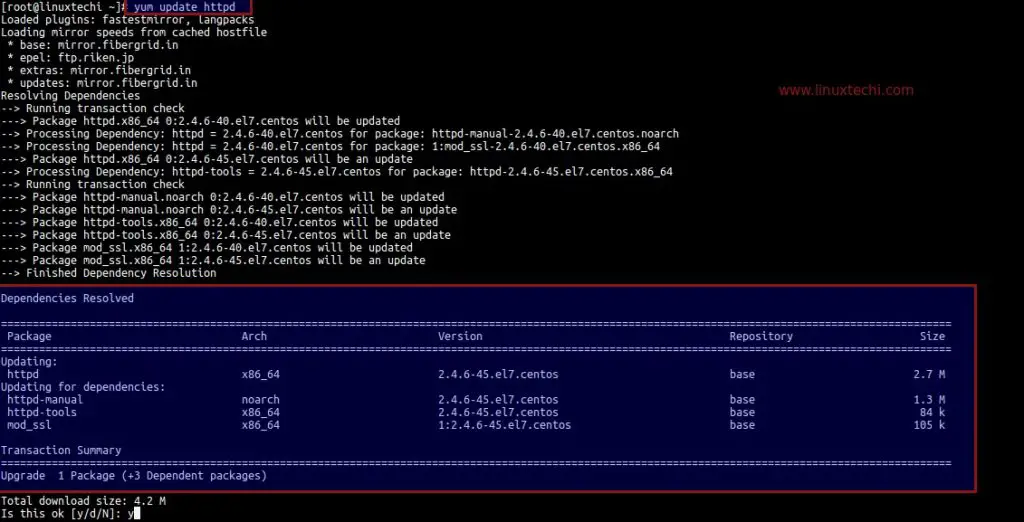
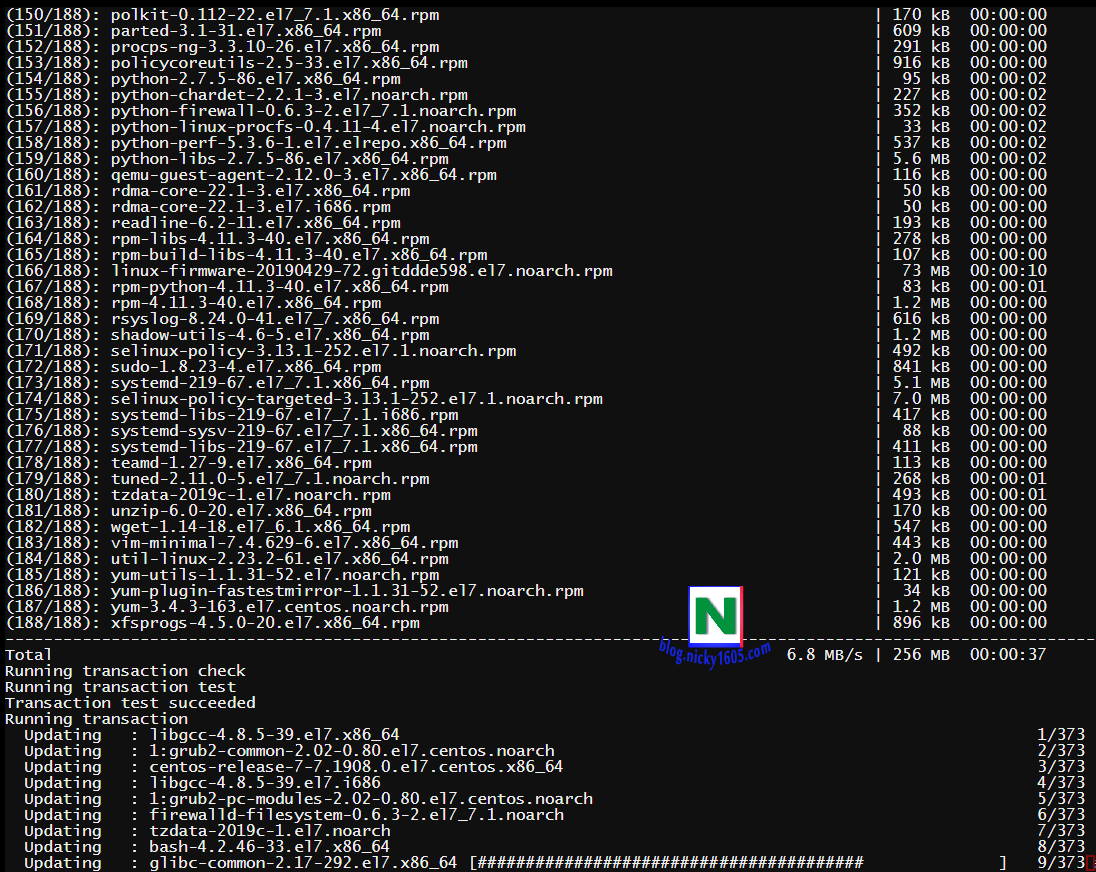
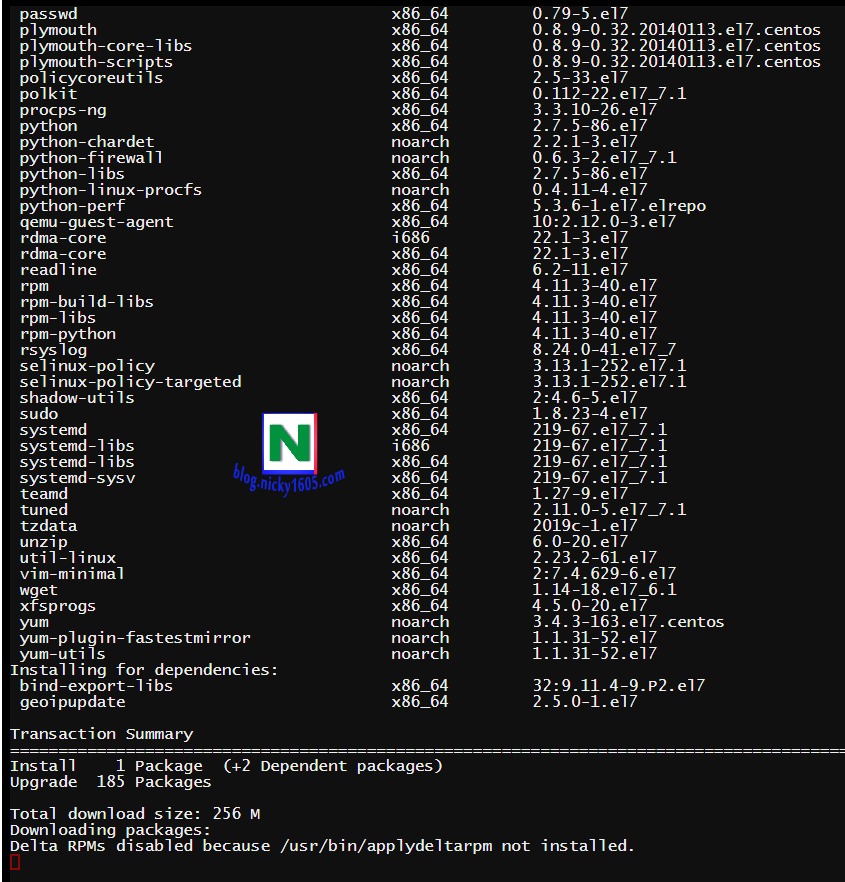
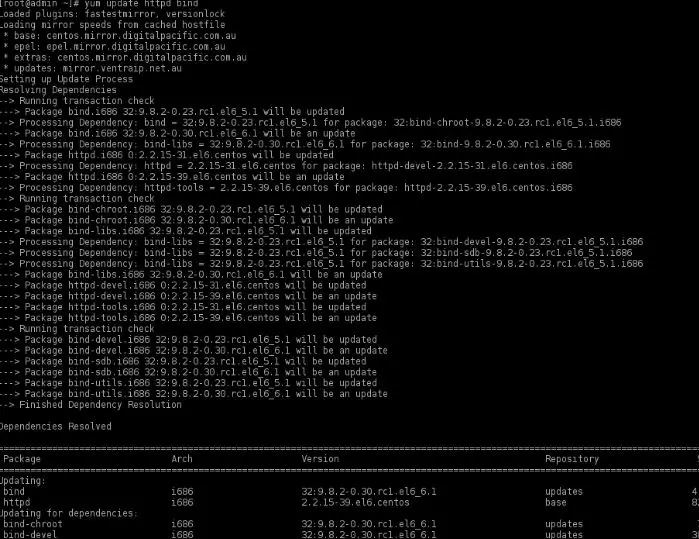
How to stop yum update. The way to do this is to find a mirror that has a specific 5.4 repository and point yum at that instead of the default configuration of pointing at a repository for. Open and edit the yum.conf file, which is located in /etc/yum.conf or in /etc/yum/yum.conf. 1 how does yum update work?
There are two > databases involved here, the rpm database. For example, if i want to exclude all. The command yum clean > only cleans cached data like, metadata, packages etc.
You can also exclude more than one package by specifying the list of packages separated by comma. The following will behave exactly same as above. 5 update a single package.
Or you can kill it, your choice. 3 update from a local repo. To exclude (disable) specific package updates, open file called /etc/yum.conf or /etc/dnf/dnf.conf with your choice of editor.
Systemctl disable packagekit. Read more about dnf here. Exclude=php* kernel* at the end, it should look like as follows:
Append/modify exclude directive line under [main]. Table of contents hide. In order for this to work, the previous versions of any packages in the transaction must exist in.
Open /etc/yum.conf file, enter: Open /etc/yum.cnf or /etc/dnf/dnf.cnf, depending on whether you want to disable updates from yum or dnf. Yum is the primary package management tool for installing, updating, removing, and managing.
Preventing yum from updating the kernel. However, if you don't ever want to just blindly have the kernel updated, you can add the following to your /etc/yum.conf file:. And isn't this the same ancient rhel system.
Generally, the options are the same. You can undo a yum update by undoing the relevant transaction (s).